Share this Post
PUBLISHED
November 28, 2022
READ TIME
9 Minutes
WRITTEN BY
![]() Dina Adlouni
Dina Adlouni
Dina is the resident Content Writer at EcoOnline North America . When she’s not writing about health and safety, you’ll find her enjoying a cup of tea while watching her favorite sitcom.
Root Cause Analysis
Getting to the root cause of incidents and injuries on site or in the field, is fundamental to creating a safer workplace. It is crucial to be aware of the underlying issue(s) which may be the cause of certain incidents, so key stakeholders can start to analyze why this may be occurring and take the necessary steps to rectify it.
Root causes can come in many shapes and sizes and can have a strong butterfly effect on you and your team. We here at EcoOnline want to help you effectively identify, mitigate, and eliminate them, and understand the tools available to help simplify this process. Read on to learn more about:
- What is root cause analysis (RCA)
- Core principles of root cause analysis
- What are the 5 steps of root cause analysis
- Tools and methods for root cause analysis (RCA)
- Example of root cause analysis
- Why choose EcoOnline
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Before we jump into the deep end, let’s take a step back and define the term root cause analysis or RCA. Root cause analysis is identifying, assessing, and evaluating the reason behind certain deficiencies and problems which may occur at the workplace. These deficiencies and problems which are not aligned with your safety program or policies, are known as root causes. Root causes can be the reason for incidents, injuries, near-misses, and more. Root cause analysis is vital to protect your people and strengthen your safety program.
Core Principles of Root Cause Analysis
It’s vital that the quality of your root cause analysis is high to properly reduce incidents and injuries in the field. Here are the top three core principles of root cause analysis you should keep in mind to elevate this process:
1. Don’t blame the workforce
It can be easy to blame employees for problems and nonconformances which may occur. This is not effective and does not truly get to the root cause. It’s important to consider all elements found within the environment at the time the incident occurred and assess the incident or nonconformance from every angle.
For example, imagine a particular worker was injured due to a fall from a particular height. Instead of immediately blaming the worker for improper use of their fall equipment, instead ask what were the conditions at the time? Was proper signage or barriers put in place in that area? Has the worker received the proper training for working at heights? Have they been given instructions on what hazards may already be present in that area before starting their shift? Once the root cause is identified, you can work to eliminate it (if possible), so it doesn’t happen again.
Read our guide on the Human and Organizational Performance Approach to cultivate a stronger safety culture and strengthen your safety management system.
2. Encourage two-way communication with your team
An effective way to elevate the quality of your root cause analysis is by encouraging two-way communication with your employees. Employees must feel a sense of psychological safety to comfortably express their thoughts and opinions at the workplace. This can help them speak freely whenever an incident or near miss occurs to help you uncover any hidden deficiencies which you may not be aware of. Take the time to listen and learn from their feedback, as they are closest to the hazards daily.
Remember, it’s a two-way street so don’t forget to always share your findings with key stakeholders and your teams. It is vital they are aware of the possible causes behind a recent incident or nonconformance and what was done to mitigate it.
3. Put corrective actions in place
Finally, though this may seem obvious, it is vital that you put corrective actions in place once the root cause has been identified. Make sure you have sufficient evidence to prove the root cause which has been identified, and assess the best course of action to mitigate it. This can be done by collaborating with key stakeholders to find the best approach to reducing this risk in the future.
Examine the hierarchy of controls and evaluate which controls would be best for this particular situation. Are new engineering controls the answer? Does this involve a policy change? Can a particular piece of equipment or tool be substituted with another? Take everything into consideration so you can implement the best course of action to prevent or mitigate this risk.
What are the 5 Steps of Root Cause Analysis
Now that you know some core principles of this process, let’s get into the 5 steps of root cause analysis. Follow this approach to effectively reduce incidents and injuries on site and create a safer workplace.
1. Acknowledge the problem
The first thing that must be done is acknowledge the problem. Understand what did not go to plan and the consequences of this deficiency.
2. Collect data and keep a record
Next, it’s important to gather as much data as you can relating to this issue. Speak to those who may have been involved in the event and employees who have job tasks related to this area, to get their opinion about what might really be going on. Record who may have been involved, what the consequences were, if this has happened before, etc. Keep this information on hand to be able to refer to, when you need it.
3. Assess the environment and all possible contributing factors
It’s important to visit the area where the problem or incident may have occurred on site. Evaluate what may have led to this issue, including elements found within the environment at the time. Keep in mind, it may not be one issue, but multiple factors at play.
4. Uncover the root cause or causes
Now, it’s time to uncover the root cause or causes behind this problem. Evaluate and analyze all the information you have gathered in the previous steps to get to the root cause of why this problem occurred.
5. Put corrective or preventative actions in place
Once the root cause or causes have been identified, you can now work towards putting corrective or preventative actions in place. This is a team effort and should not be one person’s responsibility, so collaborate and execute a plan together to effectively rectify this problem.
Tools and Methods for Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
There are many methods and tools used for root cause analysis. Find which works best for you or use several in tandem to help you get the information you need to properly protect your people.
Here are just some of the methods and tools that can be helpful:
1. Five whys
One of the most popular methods is the 5 Whys. This involves asking why five times to get to the root cause of the problem. The principle behind this method is to strip away all the superficial factors which may be the reason for an incident or injury, to get to the very source. Each time the question why is asked, you will get closer and closer to the root of the problem.
2. Failure mode and effect analysis
Failure mode and effects analysis or FMEA can help you stay proactive. This method is meant to analyze possible failures or deficiencies that may occur, what the cause for each may be, and their potential effects. This helps you stay proactive because you are outlining everything that could be a hazard and working to mitigate it before it occurs. This is helpful when you are rewriting and implementing a new process or policy.
3. Fishbone diagram
Known as the fishbone or cause effect diagram, this method can also help professionals get to the source of problems. In this method, key stakeholders consider one specific problem and all the possible causes which may have led to it. This is visually displayed with causes grouped into broad categories such as machine, processes, people, management, suppliers, and so on. Once everything is laid out and the problem is assessed from all angles, your team can begin to pinpoint areas of concern and work towards rectifying them.
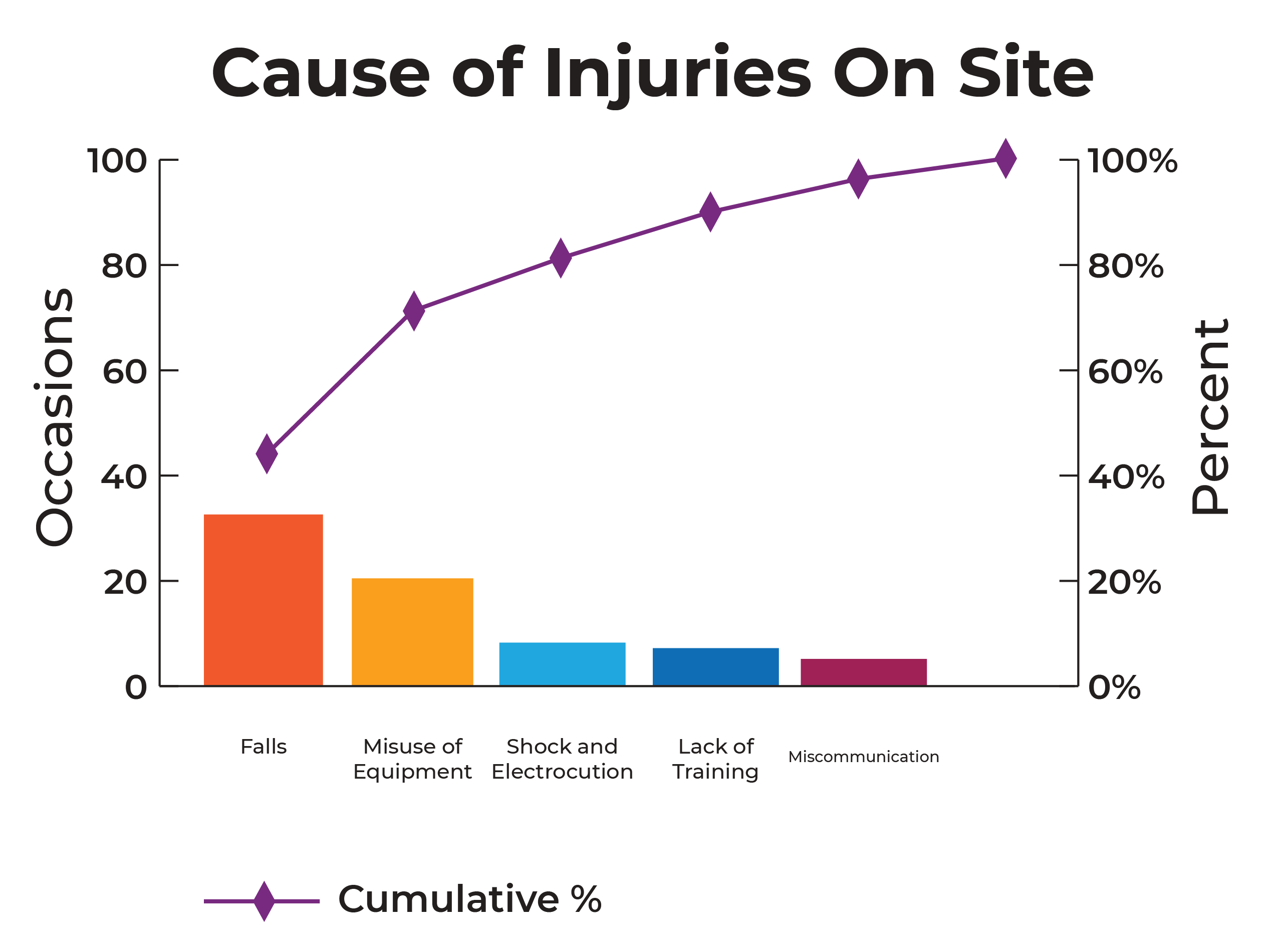
4. Pareto analysis
Pareto analysis is best when you are trying to analyze data to help you prioritize problems to tackle. Made up of both a bar chart and a line graph, pareto charts display multiple causes of an issue shown in descending order with a bar chart, and a line graph showcasing the cumulative percentages of each.
It can look something like this:
5. Change analysis
Change analysis is a method that is mostly commonly used in tandem with another to get to the source of an issue. This involves analyzing all the possible causes for a particular issue and categorizing them into different groups such as contributing factor, unrelated factor, or possible root cause. Then we can bring in another method like the 5 Whys to gain a deeper understanding of the root cause and why it occurred.
Example of Root Cause Analysis
Now that you are aware of some of the most popular tools and methods used for root cause analysis, let’s get into more detail with an example that may be applicable to a high-risk industry. Let’s say a worker sustained a back injury due to a fall from a ladder on a construction site. For this example, we will utilize the popular 5 Whys method.
Using the 5 Whys allows you to gain a deeper understanding of what is truly happening. Let’s take a closer look at how we put this into practice below:
Supervisor: Why did you fall from the ladder?
Worker: The ladder wasn’t properly secured.
Supervisor: Why wasn’t it properly secured?
Worker: I never learned how to do that.
Supervisor: Why didn’t you learn how?
Worker: My manager never trained me on it.
Supervisor: Why didn’t you receive training?
Worker: Because ladder safety isn’t part of our training before coming on site.
Supervisor: Why isn’t it part of your training before coming on-site? It’s within our policy.
Worker: Because everyone assumes its common knowledge and it isn’t enforced by management.
As you can see, we have gotten to the root cause of the injury which is that ladder training isn’t seen as important and is not part of on-site training. Key stakeholders can now take the necessary steps to make sure it is part of training and always enforced by management.
Why Choose EcoOnline?
The EcoOnline EHS management solution can help streamline your root cause analysis process, allowing you to get to key deficiencies quickly and efficiently. This is with the help of dynamic capabilities including:
- The ability to digitize and centralize all recorded incident data into one easily accessible location. This makes comparing data simple and gives you deeper insight into your safety performance and gaps found withing your safety program when conducting your root cause analysis.
- A robust reporting engine which allows you to choose from 23+ pre-built dashboards and gives you the ability to customize your own reports to gather the data you need during this process.
- The ability to continue working uninterrupted with a mobile and web platform, reducing manual time-consuming processes when analyzing multiple root causes and factors
- A corrective actions module which makes it easy to assign corrective actions once the root cause is identified, complete with priority ratings, specific assignees, images, due dates, and the ability to monitor the status of completion
- The ability to set regular reminders and alerts to key stakeholders of recurring actions which must be completed at regular intervals
- And so much more!
To learn more about how EcoOnline can help simplify your root cause analysis process, fill out the form below or speak to an EcoOnline representative.
Learn How You Can Get EcoOnline
Complete this form and one of our safety experts will be in touch.